Hell-Vollhard-Zelinsky Reaction
Description: The Hell-Vollhard-Zelinsky [HVZ] reaction is a means of converting a carboxylic acid to a brominated carboxylic acid (the bromine ends up on the alpha carbon of the carboxylic acid).
The rest of this page is available to MOC Members only.
To get access to this page, plus over 2500 quizzes, the Reaction Encyclopedia, Org 1 / Org 2 summary sheets, and flashcards, sign up here for only 30 cents/ day!
Real-Life Examples:
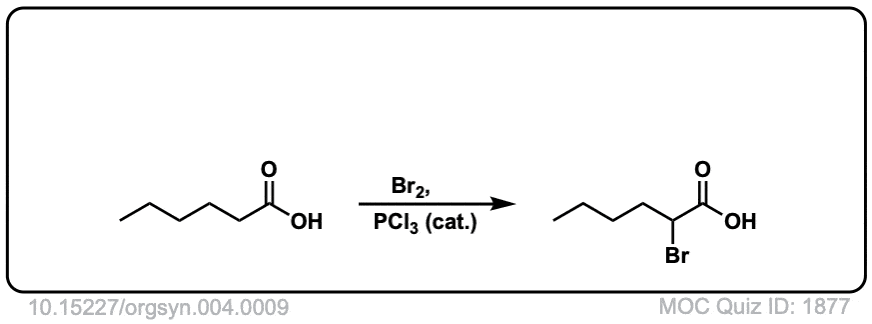
Org. Synth. 1925, 4, 9
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.004.0009
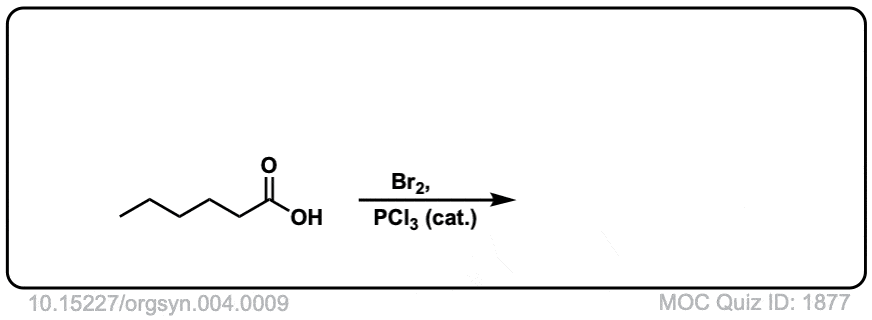 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
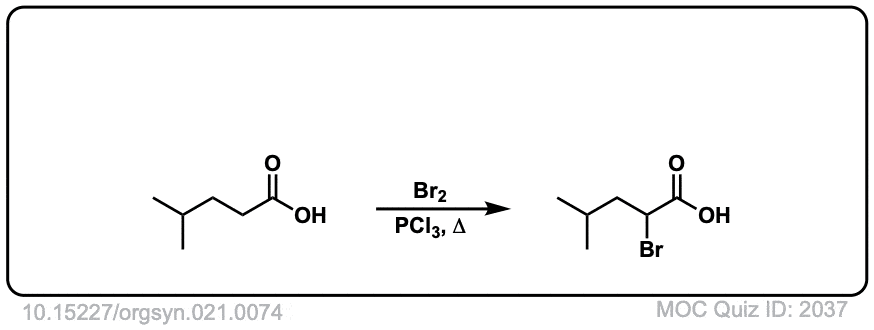
Org. Synth. 1941, 21, 74
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.021.0074
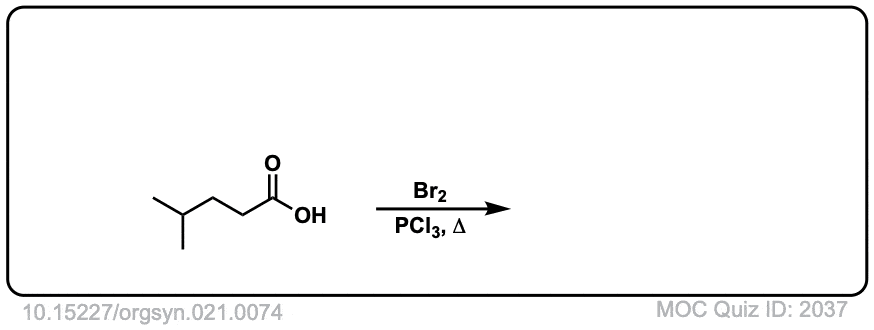 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
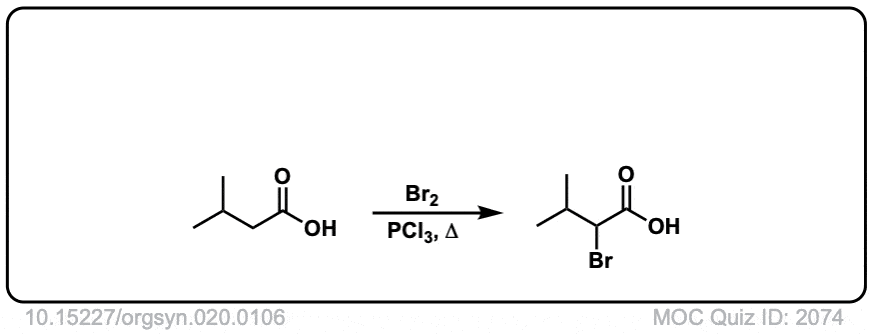
Org. Synth. 1940, 20, 106
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.020.0106
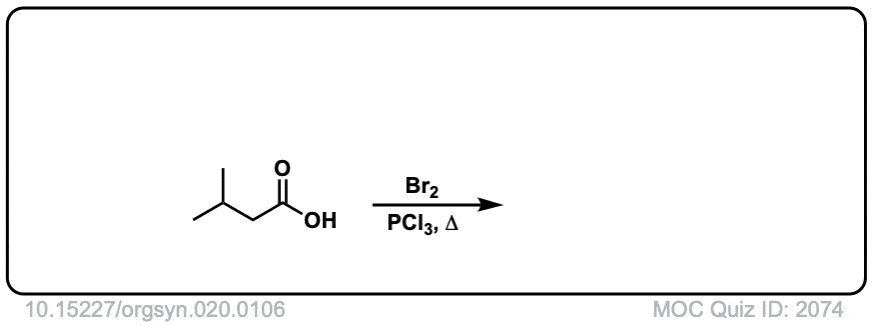 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
Org. Synth. 1959, 39, 19
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.003.0029
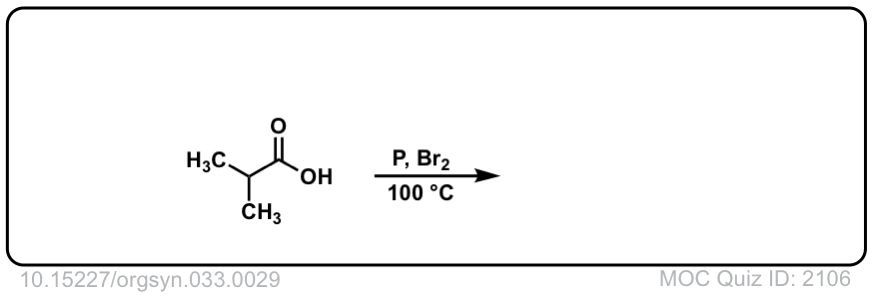 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
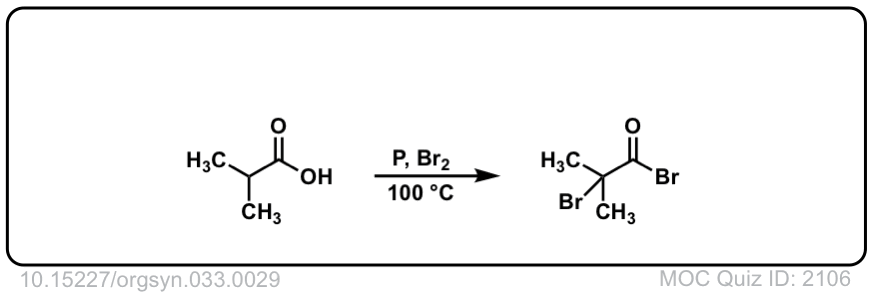
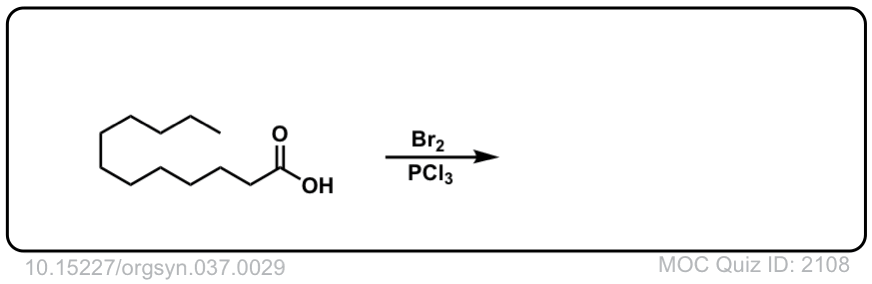
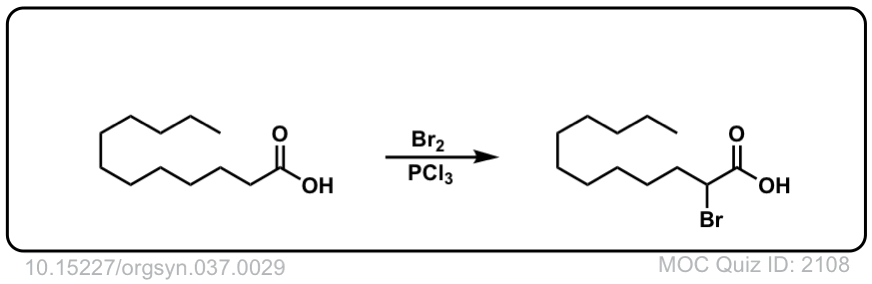
Org. Synth. 1957, 37, 29
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.037.0029
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
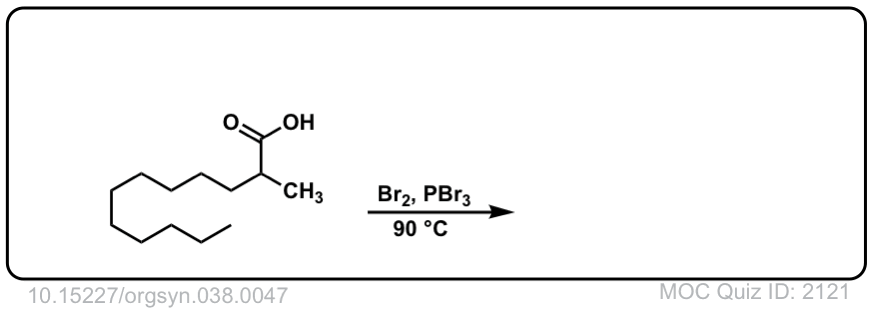
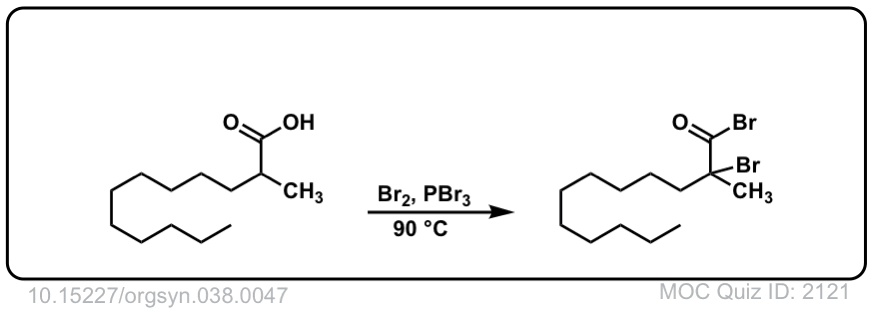
Org. Synth. 1958, 38, 47
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.038.0047
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
When we add water in the last step, why is the Chlorine not replaced by OH group?
Is it because the carbocation formed is unstable?
Water is added in the last step to convert an acid halide to the carboxylic acid. But it will generally not break the alkyl C-Cl or C-Br bond.
what would happen to the brominated carboxylic acid product if you next added H3O+ ?
Probably not that much. Over time, you might start getting replacement of the Br with OH, but that would require water acting as a nucleophile. With enough heat you might start to eliminate to give the double bond. However both of these are going to be fairly slow reactions.
If heat is present as well, you have carboxylic acid + H3O+ + heat = decarboxylation, giving you an alkyl halide?
hell-volhard-zElinsky
Oops. Thanks